|
Outline
This procedure covers the proper methods for handling circuit boards.
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
|
|||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Handling Electronic Assemblies

Figure 1. Circuit board assemblies must always be handled in properly designated work areas.

Figure 2. Designated work areas must be kept free of static generating materials.

Figure 3. Work areas must be kept neat and clean.

Figure 4. When not being worked on, sensitive components and circuit boards must be enclosed in shielded bags or boxes.

Figure 5. Whenever handling a circuit board assembly, the operator must be properly grounded using wrist strap connected to earth ground.

Figure 6. Or wearing two heel grounders and have both feet on a static dissipative floor surface.

Figure 7. Circuit board assemblies should be handled by the edges.
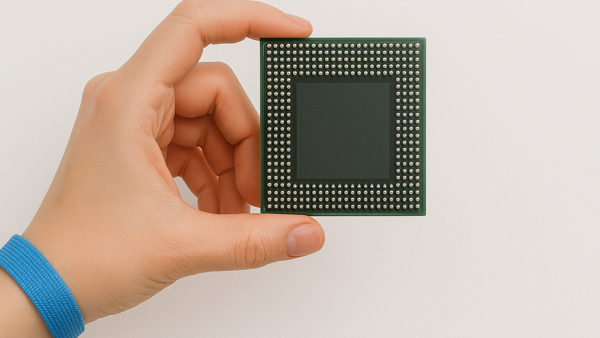
Figure 8. Components should be handled by the edges when possible.

Figure 9. Hand creams and lotions containing silicone must not be used
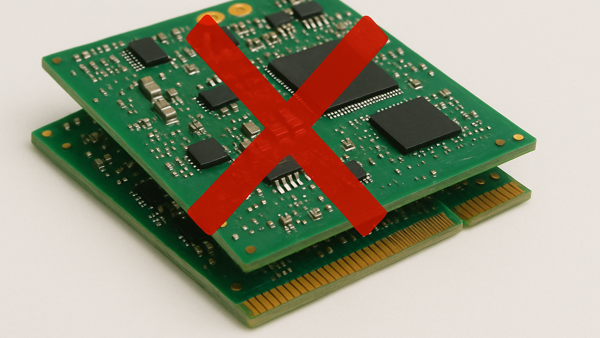
Figure 10. Stacking of circuit boards and assemblies should be avoided to prevent physical damage.
|
|||||||||||||||||
2.1 Handling Electronic Assemblies
Procedure covers ESD, EOS, safe work areas and handling and storage methods.
Minimum Skill Level: Intermediate
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Handling Electronic Assemblies

Circuit board assemblies must always be handled in properly designated work areas.

Designated work areas must be kept free of static generating materials.

Work areas must be kept neat and clean.

When not being worked on, sensitive components and circuit boards must be enclosed in shielded bags or boxes.

Whenever handling a circuit board assembly, the operator must be properly grounded using wrist strap connected to earth ground.

Or wearing two heel grounders and have both feet on a static dissipative floor surface.

Circuit board assemblies should be handled by the edges.

Components should be handled by the edges when possible.

Hand creams and lotions containing silicone must not be used

Stacking of circuit boards and assemblies should be avoided to prevent physical damage.

We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯





